4 Connecting Imagine via network
At this moment we know:
- Connect two imagines together locally - on the same computer
- Send and receive simple texts and use OnReceive event
- "Change Me" dialog of the NET object.
1. Let's launch Imagine on the first computer. This computer we will call server because we will create and run a simple server project on it:
- new "NET [style server]
- net1'connect
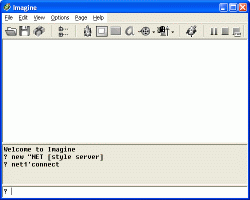
2. Now, we launch Imagine on the second computer and we create a simple client project. We start programming with familiar sequence of commands with one significant exception:
- new "NET [style client server xxx]
- net1'connect
We used to type the localhost word instead of italic xxx characters - but, because the server project is running on different computer we must replace xxx with:
- A name of the server computer on which the server project is running;
- Or an IP address of the server computer - IP address is a group of numbers which identify the computer.
3. We made small break and we describe here how to find a computer name or an IP address. Information in this paragraph is important for developers, teachers and peoples that create server version of project.
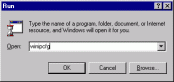
A. How to find IP Address under Windows 95, 98:
 |
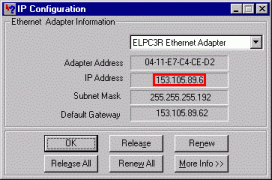 |
| Go to the "Start" menu and choose Runů Type winipcfg into edit box and press OK button. This application displays currently assigned IP address and additional information about status of network. | |
B. How to find IP Address under Windows 2000 and Windows XP:
 | |
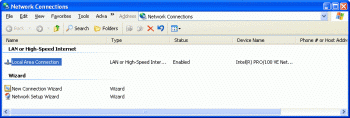
| 1. Right click on the "Network" icon on the desktop and choose Properties command | |
 |
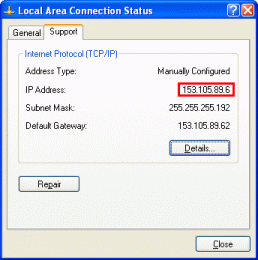 |
| 2. Double-click on Local Area Connection | 3. The IP address is displayed on the "Support" tab-sheet |
C. It is possible to use the Command Line shell under Windows 2000 and Windows XP, too:
 | |
| 1. Go to the "Start" menu and choose Runů Type cmd into edit box and press OK button | |
 |
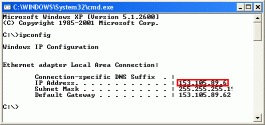 |
| 2. In the shell window type ipconfing and press Enter. This will displays current IP address | |
D. Computer name under Windows 2000 and Windows XP we find in "My Computer":
 |
| 1. Right click on the "My Computer" icon on the desktop and choose Properties command |
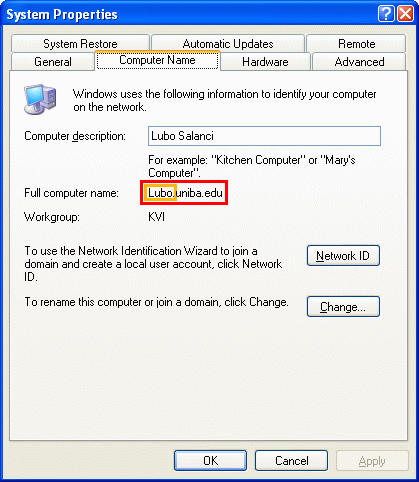 |
| 2. A computer name is displayed on the "Computer Name" tab-sheet. This name have several parts separated by . (dot) mark. It is possible to use a short part of computer name in a local network. |
From the previous description we know that:
- Our computer has IP number 153.105.89.6 - this is nearly always working (please, ask your network administrator for details about your this)
- The computer name in our subnet is Lubo - we often use this part of the name for small experiments within one computer room
- The full computer name in the Internet is Lubo.uniba.edu - this always works.
4. Now, we know the name of our server. So we may continue with creating (modifying) the client application. On the second computer we may type:
- new "NET [style client server 153.105.89.6]
- net1'connect
- new "NET [style client server Lubo]
- net1'connect
- new "NET [style client server Lubo.uniba.edu]
- net1'connect
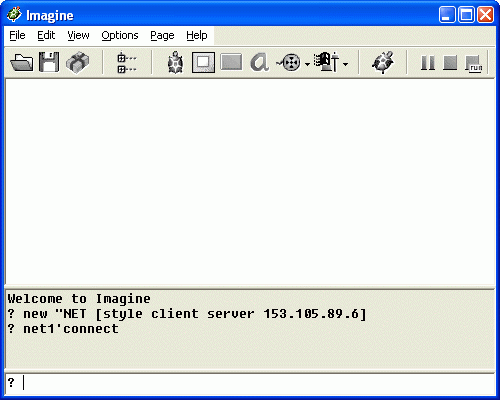
At this moment it is possible to send data via real network using:
- Command net1'send [] [Text]
- Command sh net1'message
- Event OnReceive to automatically process received message.